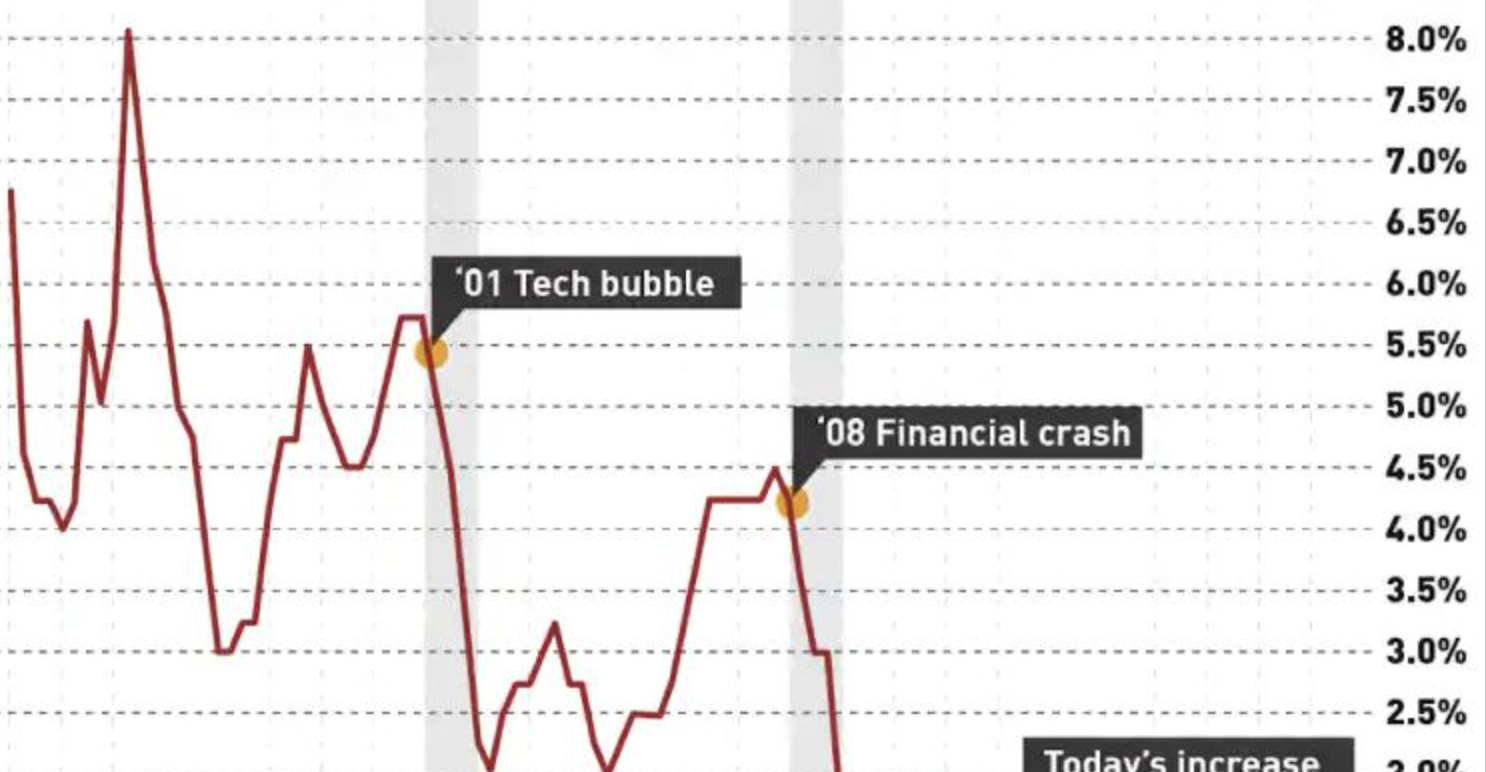
As one of Canada’s largest cities and a major economic hub, Toronto is not immune to the effects of inflation. Inflation refers to the sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services over time, resulting in a decrease in purchasing power. Understanding the causes and impacts of inflation is crucial for Torontonians to make informed financial decisions and navigate the city’s dynamic economic landscape.
Causes of Inflation in Toronto
Several factors contribute to inflation in Toronto, similar to other cities around the world. Here are some key causes:
- Demand-Pull Inflation: When demand for goods and services exceeds supply, it leads to demand-pull inflation. In Toronto, a growing population, robust tourism, and strong economic growth can drive up demand for housing, transportation, and other consumer goods, leading to higher prices.
- Cost-Push Inflation: Rising production costs, such as labor, raw materials, and energy, can result in cost-push inflation. Toronto’s high cost of living, including high housing costs, labor costs, and utility costs, can put pressure on businesses to increase prices to maintain profitability.
- Exchange Rate Fluctuations: Toronto’s economy is heavily influenced by international trade, and changes in exchange rates can impact import prices. A weaker Canadian dollar can increase the cost of imported goods, such as fuel, food, and consumer products, leading to inflation.
- Government Policies: Changes in government policies, such as changes in taxes, tariffs, and regulations, can affect production costs and consumer prices. For instance, changes in minimum wage laws or environmental regulations can impact costs for businesses, which can be passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices.
Impacts of Inflation in Toronto
Inflation can have wide-ranging impacts on Torontonians and the local economy. Here are some notable effects:
- Reduced Purchasing Power: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money, as prices increase faster than wages. This means that Torontonians may need to spend more to buy the same goods and services, reducing their overall standard of living.
- Impact on Savings and Investments: Inflation can also affect savings and investments. If the rate of inflation exceeds the rate of return on savings or investments, it can erode the value of those savings or investments over time. This can impact long-term financial planning and retirement goals.
- Housing Affordability Challenges: Toronto’s real estate market has been known for its high prices, and inflation can exacerbate housing affordability challenges. As housing costs rise due to inflation, it can become even more difficult for Torontonians, especially first-time homebuyers, to afford a home or secure affordable rental housing.
- Business Costs and Profit Margins: Inflation can impact businesses as well. Rising costs of production, such as higher wages, raw materials, and operating expenses, can eat into profit margins. To maintain profitability, businesses may be forced to increase prices, reduce costs, or cut back on investments, which can impact economic growth and job creation.
- Uneven Distribution of Impacts: Inflation may not affect all Torontonians equally. Some groups, such as fixed-income retirees or low-income households, may be more vulnerable to the impacts of inflation, as they may have limited ability to absorb rising costs. This can exacerbate income inequality and social disparities in the city.
While inflation is a complex economic phenomenon, there are ways to manage its impact on personal finances and the local economy in Toronto:
Budgeting: Creating and maintaining a budget can help Torontonians track their expenses, prioritize spending, and save for emergencies or future goals.